Double-parity RAID (redundant array of independent disks), also called diagonal-parity RAID, Advanced Data Guarding (RAID_ADG), or RAID-6, is a method of protecting against multiple storage drive failures by creating two sets of parity data on an array of hard disk s.. If the organization requires higher fault tolerance and data redundancy, RAID 6 may be a better choice than RAID 5. RAID 6 provides two parity blocks for each data block, which makes it more resilient to disk failures than RAID 5. Performance Needs. If the organization requires better write performance, RAID 5 may be a better choice than RAID 6.

PPT Data Protection RAID PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3571999

RAID 0 vs RAID 5 vs RAID 6 WD Red Pro 22TB and QNAP NAS 10GbE Tests NAS Compares

Ausfallsicherheit von RaidKonfigurationen Seite 3 von 4

Innovern Solutions Understanding Different RAID Levels

RAID 5 vs RAID 6 Which Is The Better RAID?

Capacity, performance and durability compared in RAID 5 vs. RAID 6. tBlog
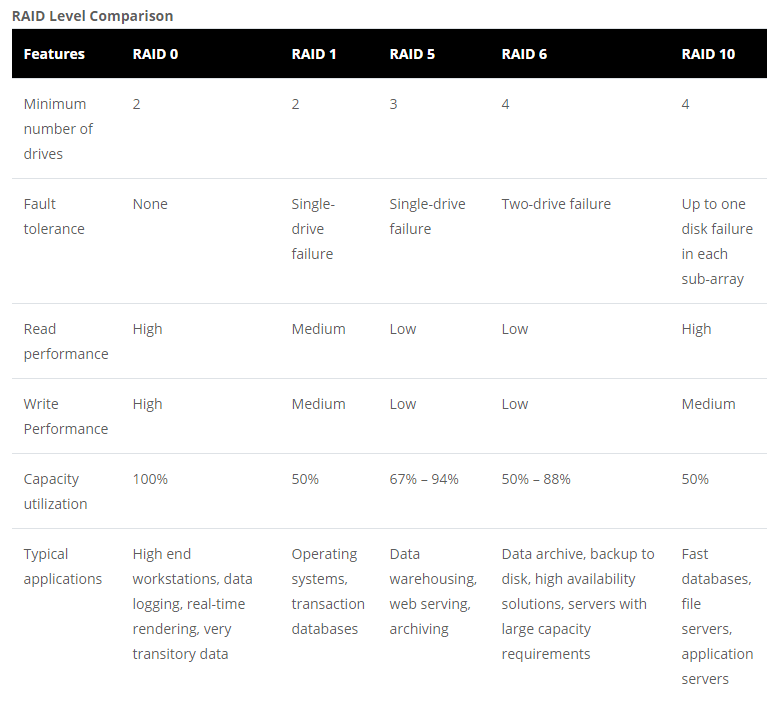
RAID Level Comparison RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 and RAID 10 Pamir Alpha Technologies
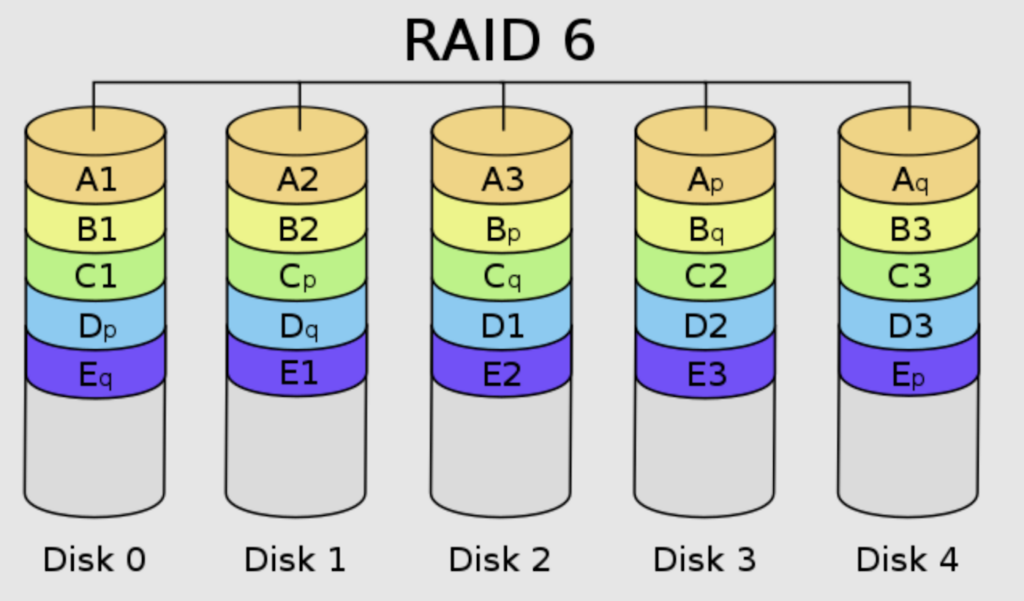
RAID 5 vs RAID 6 How to Choose the Best RAID Configuration Petri

RAID 5 vs RAID 6 Compared Which Is The Better RAID?

Raid 5 vs Raid 6 12 Most Amazing Difference Between Raid 5 vs Raid 6
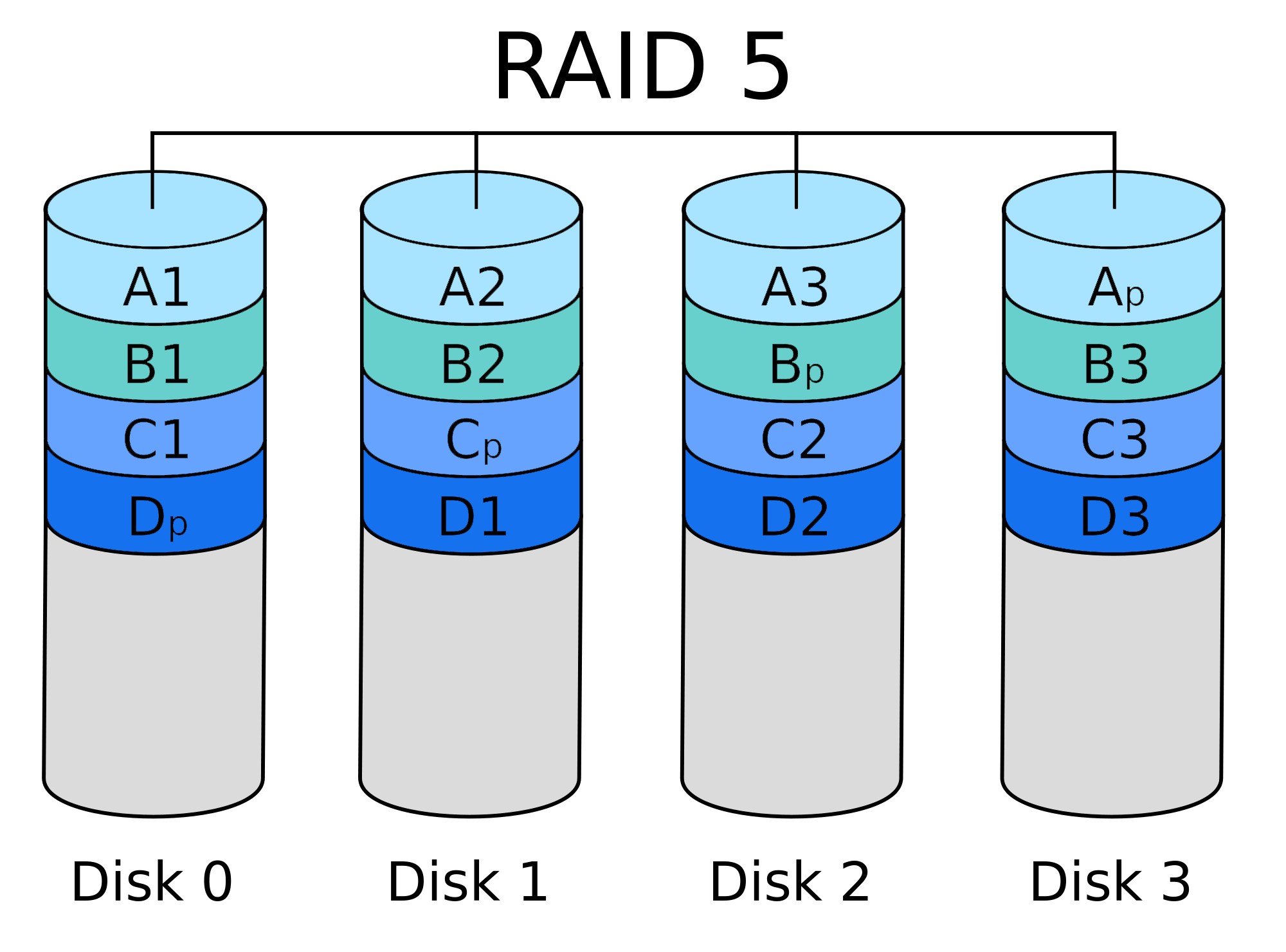
Most popular RAID levels explained Chicago Computer Repair

RAID 5 vs RAID 6 Compared Which Is The Better RAID?

Tipos de RAID cuál ofrece mejor seguridad y rendimiento en un NAS
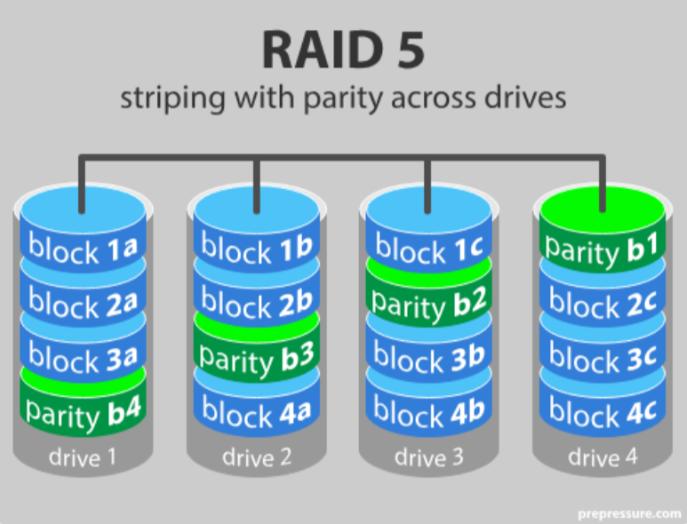
Understanding RAID The Uses, Pros and Cons of Each Level

RAID 5 vs RAID 6 Differences, Benefits and Disadvantages

RAID 5 vs RAID 6 Compared Which is the Better RAID? Itechguides

≫ Raid 5 vs raid 6 ⊛ Leve Digital
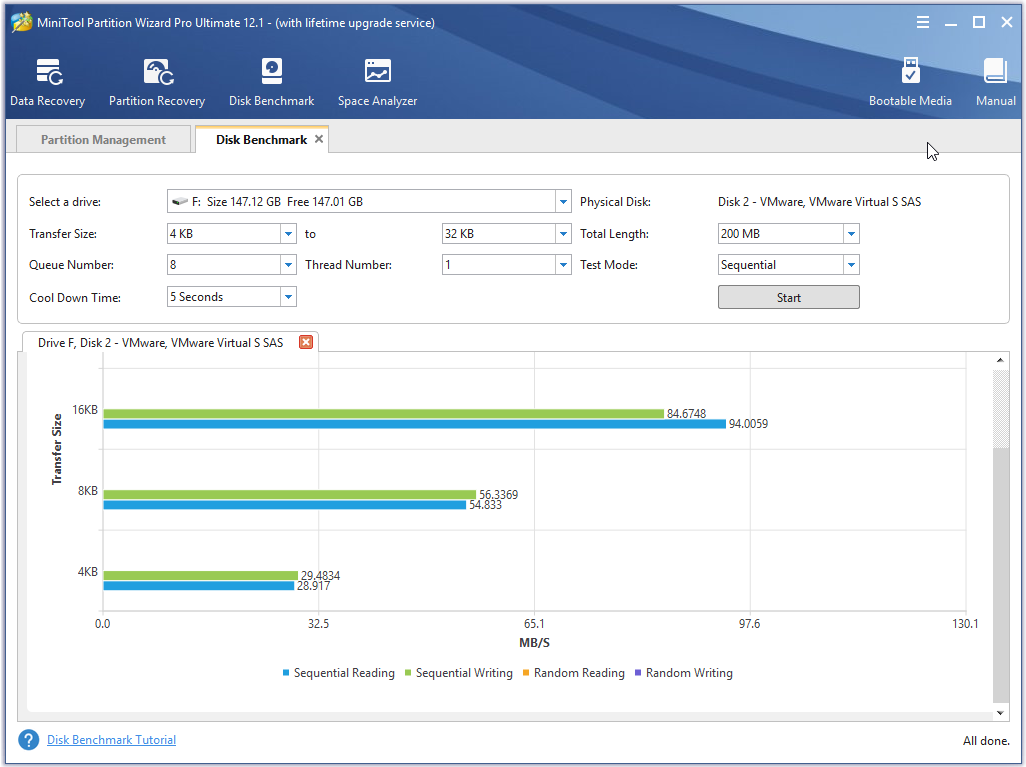
RAID 5 VS RAID 6 on Benefits, Performance, and Application MiniTool Partition Wizard

Innovern Solutions Understanding Different RAID Levels

RAID 5 vs RAID 6 Which is Better? TTR Data Recovery
RAID 5 offers more usable storage than RAID 6 by using one parity drive, distributing parity across all drives for redundancy and maximizing capacity. RAID 6 provides extra data protection with double parity at the expense of usable space. Thus, for maximizing storage, RAID 5 is the better option.. RAID 6 is a little slower than RAID 5 for write performance. Pros and Cons. Both RAID 5 and RAID 6 offer fast reads and are hot-swappable, i.e., the system is functional and continues to support reads even when a failed disk is being replaced. RAID 5 is more common than RAID 6. The advantages of RAID 5 over RAID 6 include: