Cervical polyps are small fingerlike growths originating from the mucosal surface of the cervix. The small fragile growths hang from a stalk and protrude through the cervical opening. Review Date 1/10/2022. Updated by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also.. A cervical polyp is a growth that develops on the cervix, which is the canal connecting the uterus to the vagina. Sperm must pass through this canal to fertilize an egg. Cervical polyps are tumors.

Cervical polyp on transvaginal ultrasound Ultrasound Pinterest Ultrasound and Radiology
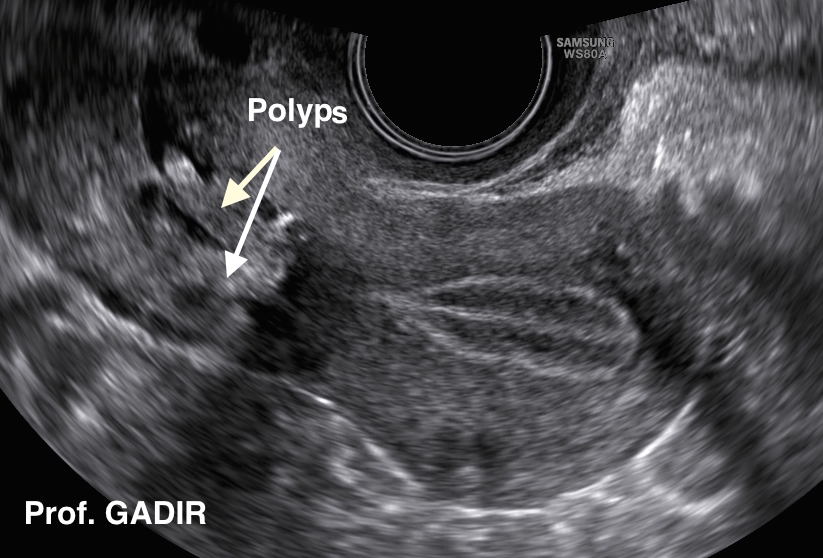
Polyps
Cervical polyp radRounds Radiology Network

Cervical Polyps Symptoms, Causes & Treatment Santripty
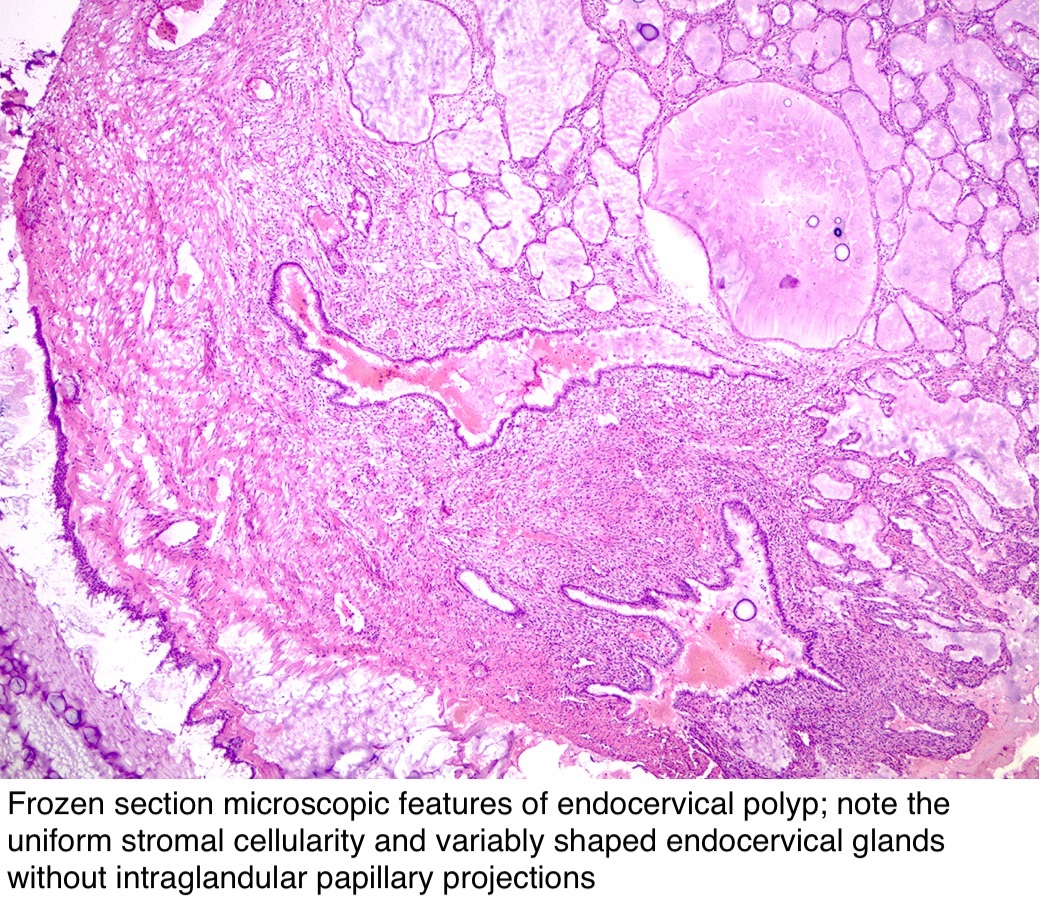
Pathology Outlines Endocervical polyp

Polyp of Cervix Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis

List of publications about giant cervical polyp. Download Table

Cervical polyp, SEM Stock Image C045/9729 Science Photo Library
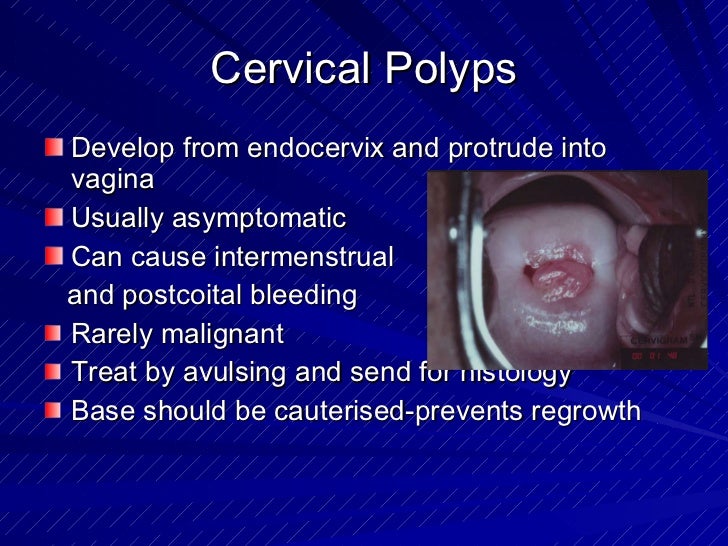
Benign lesions of the cervix, vagina and vulva

What Is a Polyp? YourCareEverywhere
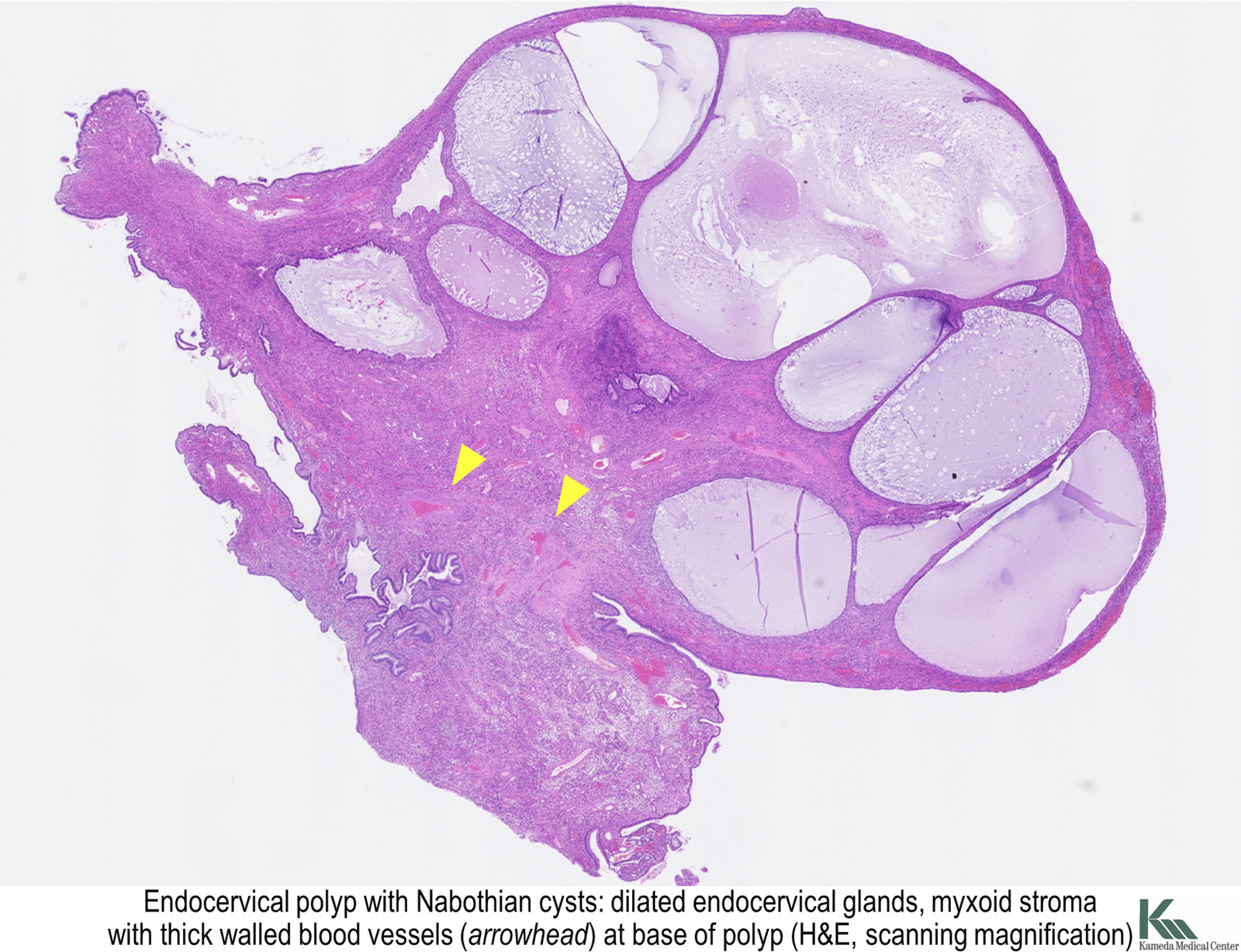
Pathology Outlines Endocervical polyp
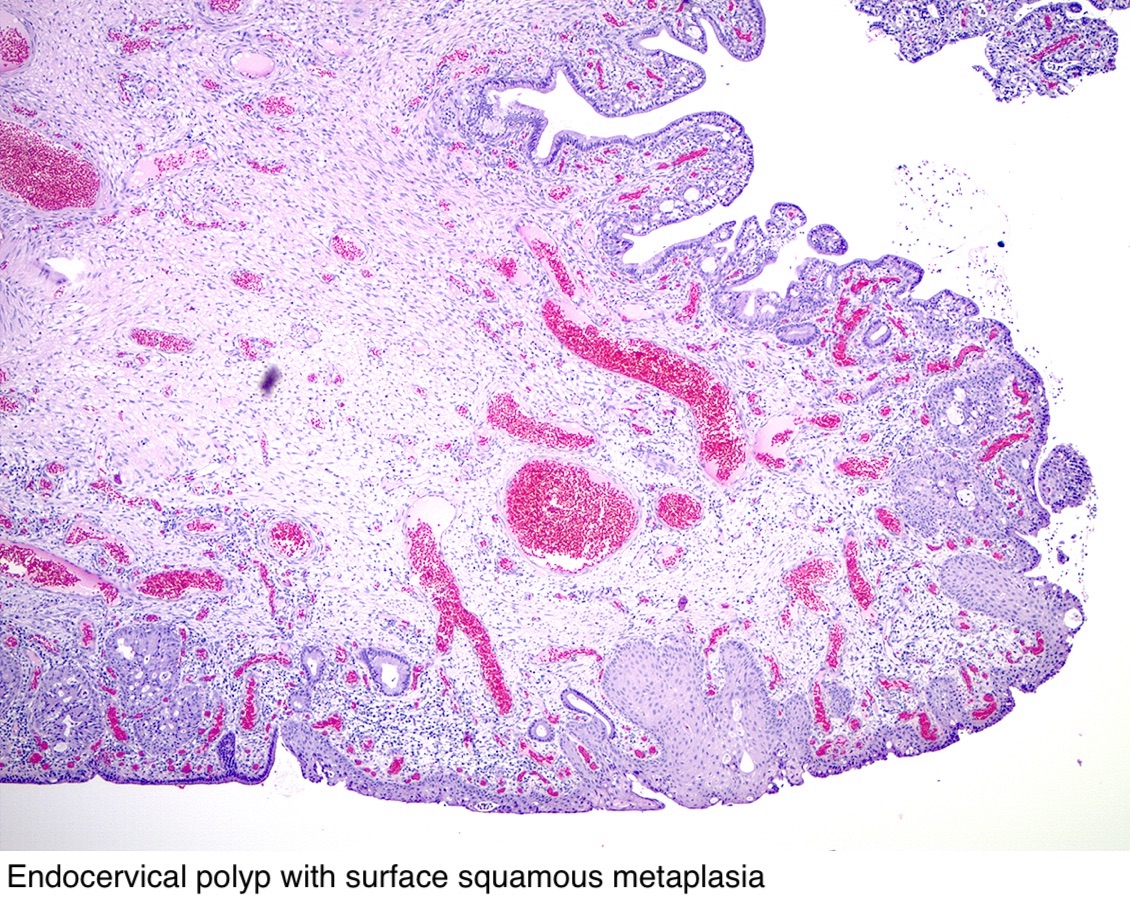
Pathology Outlines Endocervical polyp

Cervical Polyps Diseases & Conditions 5MinuteConsult
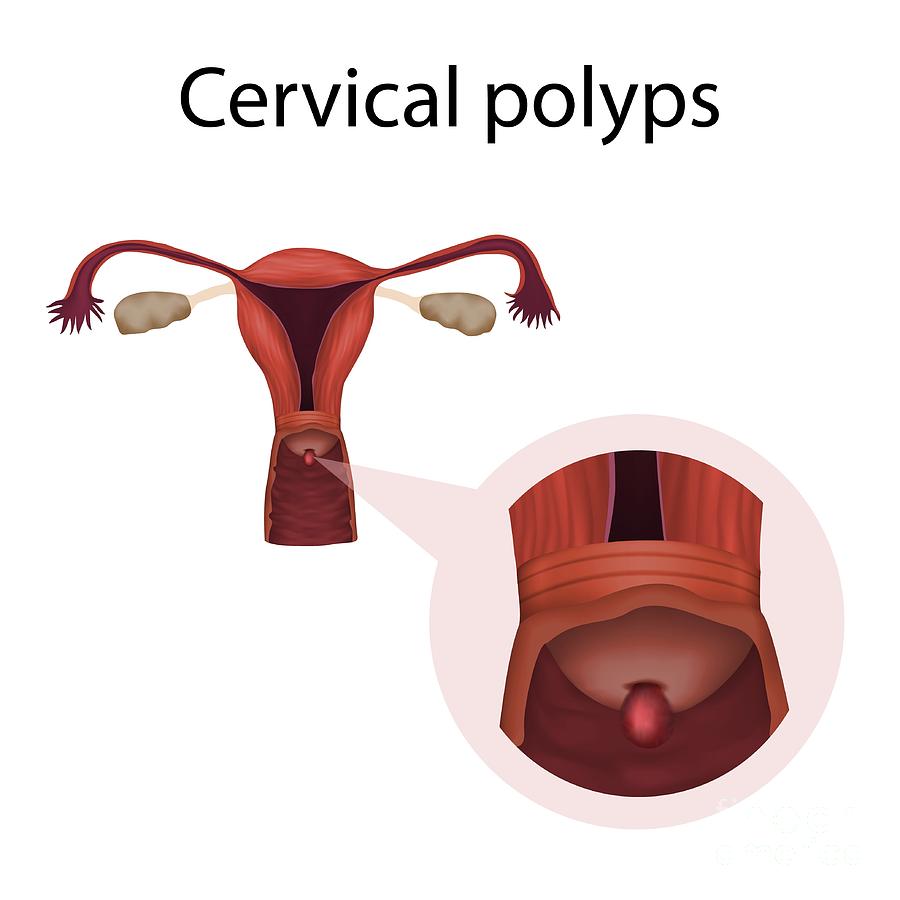
Cervical Polyps Photograph by Veronika Zakharova/science Photo Library

Cervical polyp, SEM Stock Image C045/9728 Science Photo Library
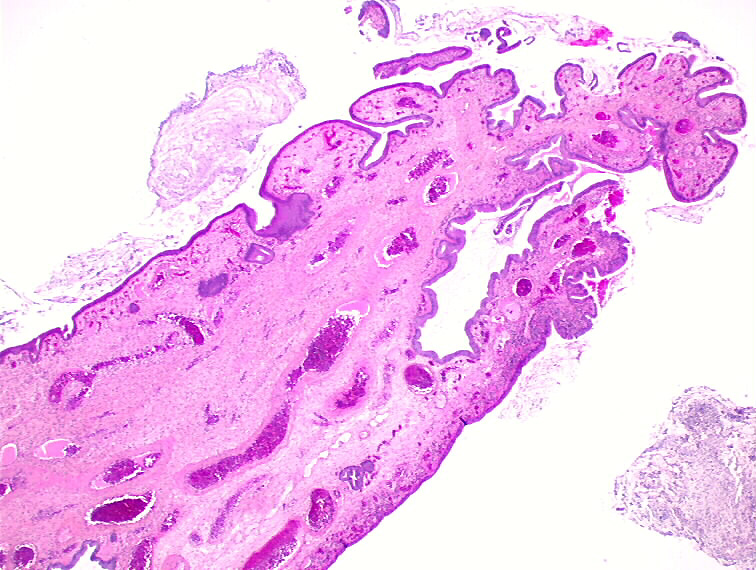
Pathology Outlines Endocervical polyp
Cervical and Endometrial polyp Cause and Treatment

ENDOMETRIAL POLYP WITH A STALK PRESENTING IN THE CERVIX Looking Through a Transducer

Cervical Polyp On Ultrasound
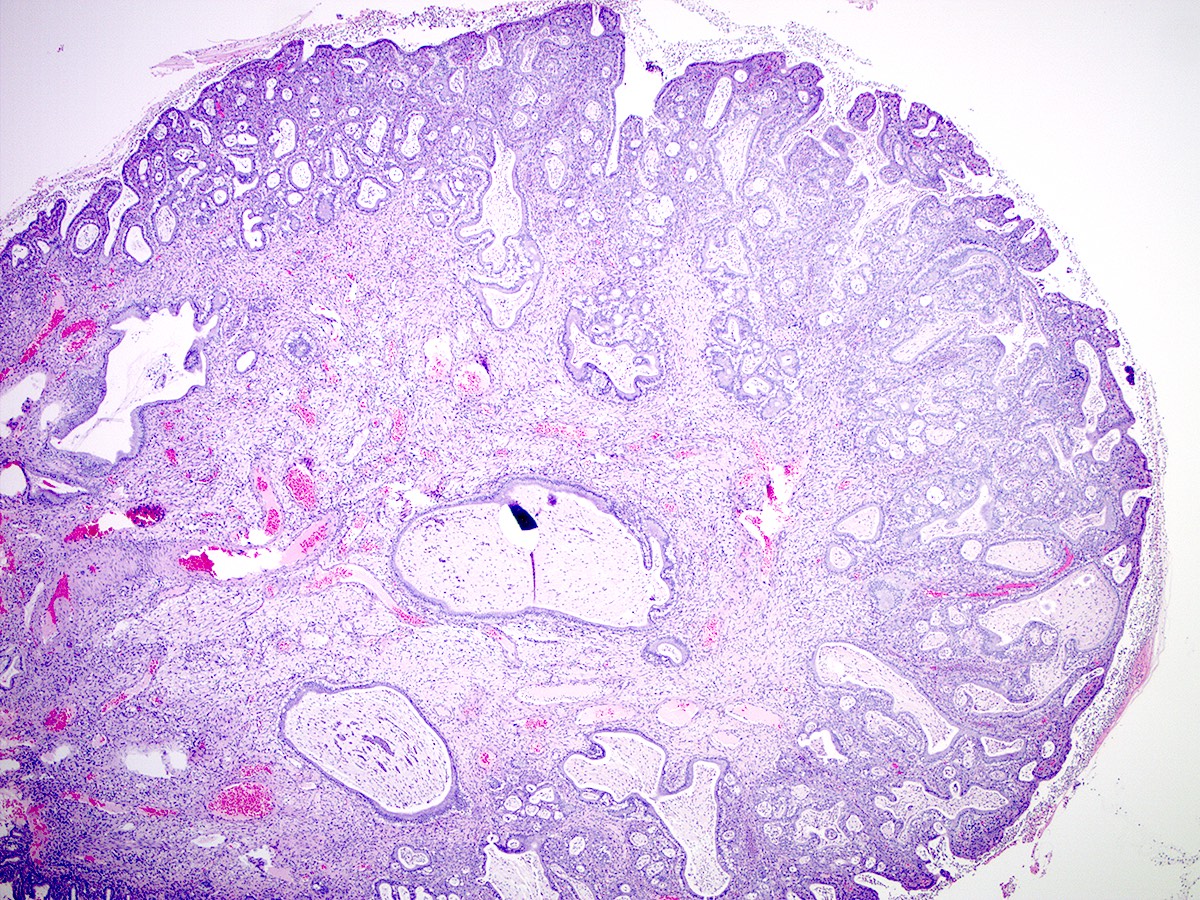
Pathology Outlines Endocervical polyp
Videos Figures Images Quizzes Symptoms View All Resources. RESOURCES 3D Models Abbreviations. A cervical polyp (bright red and round at center) is seen through a cervical speculum. DR P. MARAZZI/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY. In these topics. Cervical Polyps.. Clinical Features. Cervical polyps are often asymptomatic, identified only via routine cervical screening. If symptomatic, the most common clinical feature is that of abnormal vaginal bleeding. This can be in the form of menorrhagia, or intermenstrual, post-coital, or post-menopausal bleeding. Polyps can also cause increased vaginal discharge.